The central Nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The rest of the nervous system apart from the brain and spine is known as the peripheral nervous system. The skull and the spine are bony coverings which protect the central nervous system.
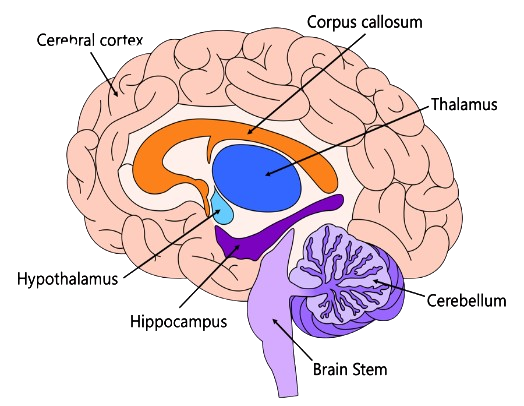
The brain is made up of three main parts: The cerebrum; the cerebellum and the brainstem. The Cerebrum interprets sights, sounds and touches. It is also a regulator of emotions, reasoning and learning. It is considered the part of the brain that differentiates humans from the other animals because of its increased complexity more than the other animals. The Cerebellum maintains balance, posture and coordination and fine motor skills. The Brainstem regulates many automatic body functions Such as heartbeat and breathing. It is sometimes referred to as the primitive brain. The different parts of the nervous system are interconnected physically so that they can coordinate and serve effectively as an effective communication system with the external and internal world.
There are many different conditions which may affect the brain. The symptoms that are seen are generally related to the part of the brain that is affected and the functions which that part of the brain performs. The approach to diagnosis of conditions of the brain is the same as the approach to the diagnosis of conditions in other parts of the body. After expressing a chief complaint the patient may then have a history and physical and then testing and imaging if necessary.
There is an almost unlimited number of conditions which may affect the brain. Some of the more common ones are headache, altered mental status, dizziness, Dementia, seizures, brain bleeds, tumors, Brain herniation, trauma, stroke etc.
Generally x-rays are not very useful for evaluating the brain because they cannot penetrate the skull effectively. Different types of CT (Computerized Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans are effective at demonstrating brain conditions.
Some modalities (types of imaging) used in the brain are known as functional imaging modalities because they show how the brain functions and not just its physical structure. An example of a function that may change or that may be different in different parts of the brain is ‘blood flow’. Functional MRI (fMRI) and Perfusion Imaging are modalities that are able to show differences in blood flow. PET (Positron Emission Tomography) and SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computerized Tomography) imaging modalities use radioactive substances to evaluate different body processes as part of functional imaging.
I know that some of this seems very complicated but when it is broken down to you in a simple and understandable way it will not seem so bad.